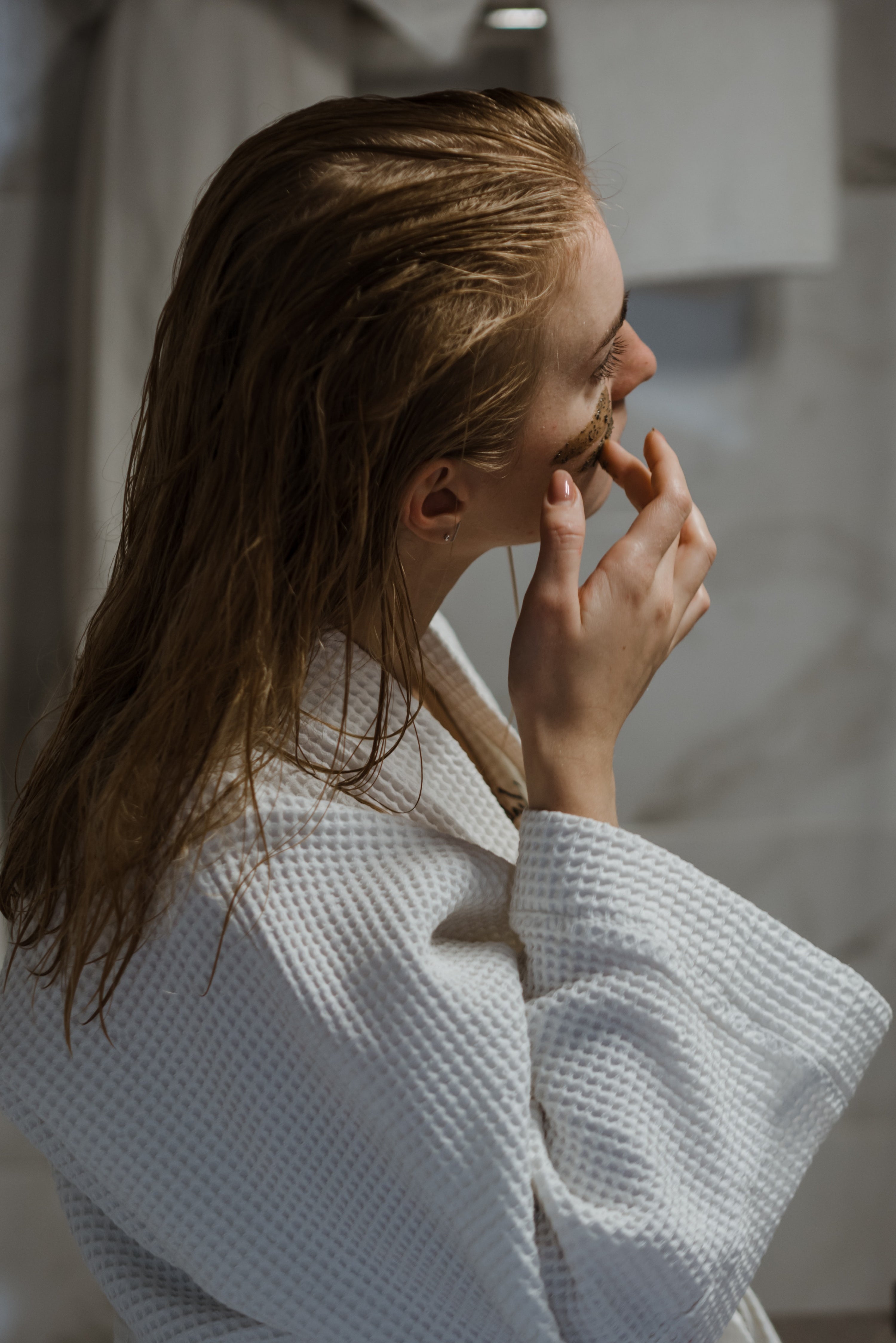
Skin exfoliation is a crucial step of every skin care routine. Exfoliation has numerous benefits such as removing dead skin cells, improving circulation, encouraing skin turnover, limiting dullness, and also allowing for better absorption of skin care products.
The absence of exfoliation could not only result in dull looking skin, but also result in breakouts and deep blackheads.
There are different methods for exfoliation. Your skin type should determine which method you use and how often you exfoliate. For certain skin conditions, including rosacea, exfoliation isn’t usually recommended.
There are 2 types of exfoliation methods;
MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL:
This type of exfoliation requires a tool such as a brush or sponge. Many scrubs are also considered mechanical exfoliators.
Many dermatologists recommend against using physical exfoliation methods, especially those that include a tool (brush/sponge), due to the risks associated with damaging the skin barrier.
When mechanically exfoliating, it’s important to be gentle on your skin. You can make small, circular motions using your finger to apply a scrub.
CHEMICAL:
This type of exfoliation method includes the use of acids and chemical peels to get rid of dead skin cells. They are also referred to as AHAs/BHAs/PHAs in product labelling.
Despite the market trend around these chemical exfoliation methods, they can damage the skin barrier drastically if not used properly. Many countries (such as Canada) regulate the use of these acids as they can cause severe damage to skin.
While choosing a chemical exfoliator, one must be aware of which acids are suitable for their skin type and condition. For instance, the use of high % of BHA on dry skin can further dry out the skin barrier and cause barrier damage.
Now, let us get into some common skin types and their exfoliation needs:
DRY SKIN
Exfoliation is one of the most important skin care steps for dry skin as they generate dead skin cells faster than other skin types. It is recommended for dry skin types to avoid mechanical exfoliation as it can cause microtears.
AHAs are effective for dry skin while Glycolic acid will help remove dead cells sitting on the surface of the skin and encourage healthy skin turnover.
*Follow up with an SPF and moisturizer after using glycolic acid. It can make the skin more prone to sun damage.
Other acids that can be beneficial for dry skin are Azelaic, Galactose, Lactic, Malic, Mandelic, Tartaric
SENSITIVE SKIN
Avoid scrubbing or using mechanical tools if you have sensitive skin. These methods will irritate your skin further and can lead to skin barrier damage.
Use a mild exfoliator such as Azelaic, Galactose, Glycolic, Lactic, Mandelic acids.
OILY SKIN
Oily skin types tend to have thicker skins and could benefit from scrubs. They can also benefit from chemical exfoliation methods.
Those with oily skin can opt in for Azelaic, Glycolic, Malic, Mandelic, Retinoic, or Salicylic acids.
NORMAL OR COMBINATION SKIN
If your skin doesn’t have any complications, you can choose any method of exfoliation. Manual and chemical exfoliation are both safe for this skin type. You may need to experiment to find out which method works best for your skin.
Combination skin may need a combination of both methods; however, they should never be used together on the same day.
The frequency of exfoliation depends highly on your skin type and the type of exfoliation you’re using. Some chemical exfoliants can be strong, for example: In general, exfoliating skin one to two times a week is enough to be effective for dry skin; however, oily skin may require more frequent exfoliation.
Avoid over-exfoliating as it can lead to redness and irritation. Talk to your dermatologist if you need help figuring out how often it’s safe for you to exfoliate.